If you are interested in energy efficiency, you may have heard of the term U-Value. But what does it mean and why is it important? In this blog post, we will explain what a U-Value is, how it is measured, and how it affects the thermal performance of your home.
A U-Value is a measure of how much heat passes through a material or a structure. It is expressed in watts per square meter per degree Kelvin (W/m2K). The lower the U-Value, the better the insulation. For example, a wall with a U-Value of 0.2 W/m2K will lose less heat than a wall with a U-Value of 0.5 W/m2K.
U-values are important for designing energy-efficient buildings, as they indicate how much heat will be lost or gained through different parts of the building envelope. By choosing materials and structures with low U-values, we can reduce the need for heating and cooling, and save money and resources.
How are U-values calculated?
U-values are calculated by dividing the rate of heat transfer through a material or a structure by the temperature difference across it. For example, if a wall has a U-value of 0.3 W/m²K, it means that for every degree of temperature difference between the inside and the outside of the wall, 0.3 watts of heat will flow through each square meter of the wall.
To calculate the U-value of a composite structure, such as a wall with multiple layers, we need to add up the thermal resistances of each layer. Thermal resistance is the inverse of thermal conductivity, which is a property of each material that describes how easily heat can pass through it. The higher the thermal conductivity, the lower the thermal resistance, and vice versa.
For example, to calculate the U-value of a cavity wall with bricks, insulation and plaster, we would do the following:
– Find the thickness and thermal conductivity of each layer
– Calculate the thermal resistance of each layer by dividing the thickness by the thermal conductivity
– Add up the thermal resistances of all layers, including the internal and external surfaces
– Find the inverse of the total thermal resistance to get the U-value
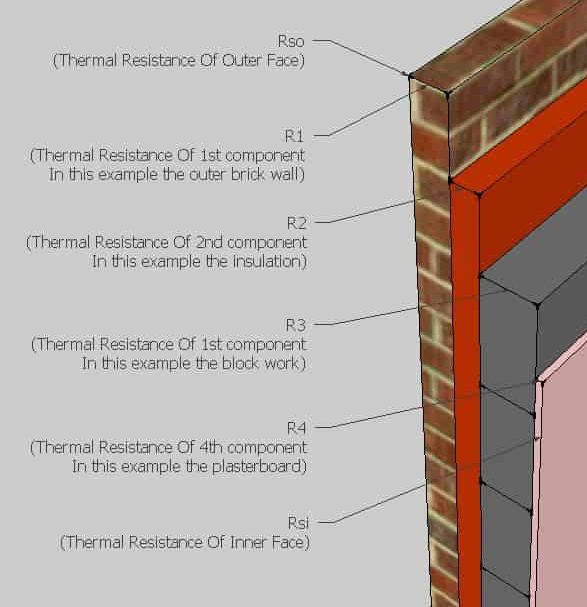
The lower the U-Value, the better the insulation.
The image shows a cross-sectional view of a wall with different layers and their respective thermal resistances labeled. The U-Value of the wall can be calculated by finding the reciprocal of the sum of all the thermal resistances of each layer, including the inner and outer faces.
The formula is:
U=1/Rsi+R1+R2+R3+R4+Rso
where:
- U is the U-Value in W/m²K
- Rsi is the thermal resistance of the inner face in m²K/W
- R1, R2, R3, and R4 are the thermal resistances of the first, second, third, and fourth components of the wall in m²K/W
- Rso is the thermal resistance of the outer face in m²K/W
To find the thermal resistance of each component, you need to know the thickness and the thermal conductivity of the material. The thermal resistance is calculated by dividing the thickness by the thermal conductivity.
For example, if the first component is a brick wall with a thickness of 0.1 m and a thermal conductivity of 0.7 W/mK, then the thermal resistance is:
R1=0.70.1=0.143 m²K/W
